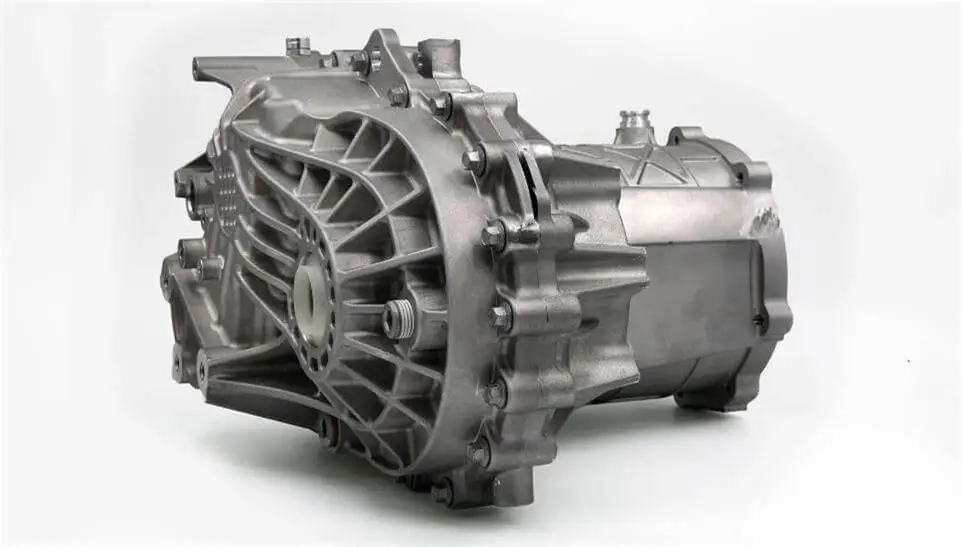
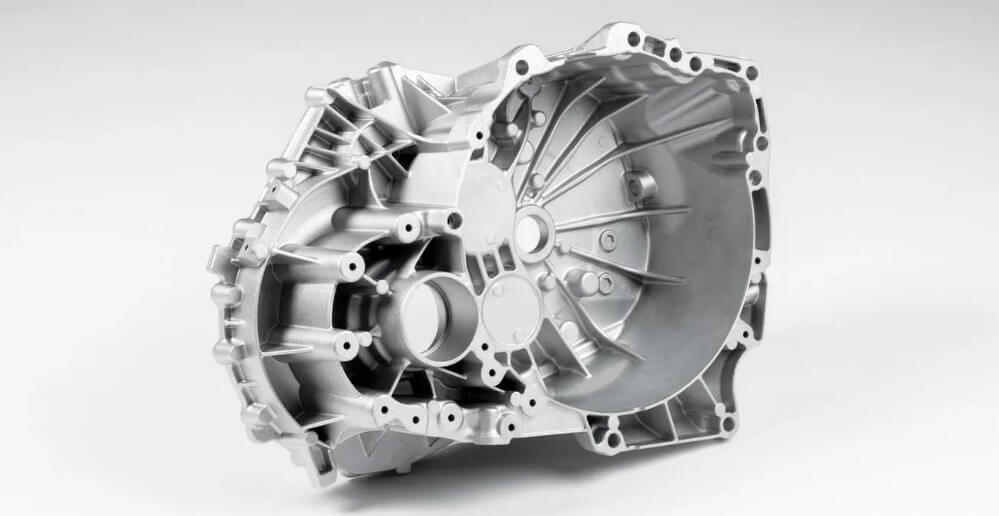
Die cast aluminum gearbox housing – from forming to one-stop post-processing
Are you looking for a gearbox housing manufacturing solution that is both light and strong, efficient and reliable? The maturity of aluminum die casting technology and the rise of integrated processing services are providing a perfect answer to this demand.
At LVXUN, we not only provide die casting services, but also provide customers with a one-stop solution that saves time, effort and cost through CNC finishing and a variety of surface treatment technologies. This article will take you to an in-depth understanding of the entire manufacturing process and process points.
Table of Contents
1.What is a gearbox housing?
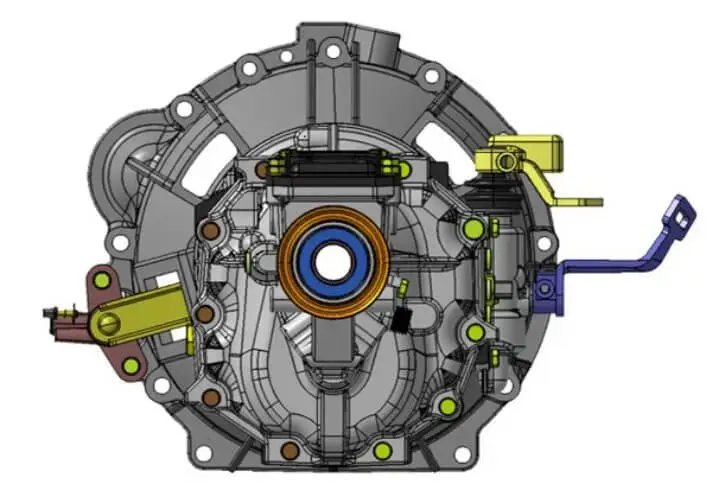
The gearbox housing is a shell structure used to cover and protect all key components inside the gearbox (such as gears, bearings, synchronizers, etc.). It plays the role of supporting and fixing the transmission system components, while also preventing oil leakage, isolating dust, and helping to dissipate heat and so on.
It is usually made of metal materials with good rigidity, such as aluminum alloy or cast iron. Among them, aluminum alloy housings are increasingly widely used in modern automobile manufacturing due to their lightweight characteristics.
Most of its structural forms are box-shaped closed structures, usually composed of two parts: the main housing and the end cover. Some designs also include a split structure of the upper and lower housings, or a combination of the left and right housings.
In addition, in some applications (such as automatic transmissions or large commercial vehicle transmissions), a bell-shaped housing structure is common, that is, one end of the housing is flared, which is used to connect the engine and the transmission system. This structure is usually die-cast in one piece, and there are also split welding or bolt connections.
2.Why choose aluminum die casting to manufacture the gearbox housing?
Aluminum die casting is a process that uses high pressure to inject molten aluminum into a precision metal mold for rapid prototyping. It is particularly suitable for the production of parts with complex structures, high dimensional accuracy, and large production batches. The main reasons for using aluminum die casting are:
Light weight: The density of aluminum alloy is about 2.7g/cm³, which is only one-third of traditional cast iron. It helps to reduce the overall weight of the vehicle, especially in line with the lightweight needs of new energy vehicles.
Forming complex structures: Die casting can form complex structures in one piece, such as ribs, oil channels, threaded holes, etc., reducing subsequent processing steps.
High production efficiency: short mold forming cycle, fast injection efficiency, especially suitable for mass production.
Good heat dissipation: Aluminum has high thermal conductivity, which can effectively help the gearbox dissipate heat, thereby extending the service life of internal parts.
3.Which aluminum alloy is commonly used?
The aluminum alloy used for die casting is mainly silicon-based aluminum alloy, which has good fluidity, corrosion resistance and weldability. Common alloys are:
ADC12 (equivalent to A383): the most commonly used die casting alloy, with excellent comprehensive performance, good castability, and suitable for complex shapes.
A380: General-purpose die casting aluminum alloy with high strength and good dimensional stability.
AlSi9Cu3 (European standard): has good thermal conductivity and thermal cracking resistance, suitable for structural parts.
AlSi10Mg (suitable for heat treatment): used in occasions requiring higher mechanical properties and corrosion resistance.
4.What are the key steps and control parameters of die casting gearbox housing?
In the process of manufacturing gearbox housing, die casting technology is widely used for its high efficiency, high precision and complex structure forming capabilities. The gearbox housing structure usually contains multiple functional areas, with complex shapes and high dimensional requirements.
Therefore, in the die casting process, the key steps and process parameters must be precisely controlled according to these structural characteristics to ensure the density, mechanical properties and dimensional accuracy of the parts.
The die casting process usually includes mold preheating → alloy melting → alloy injection → cooling and solidification → demolding → post-processing. Due to the different wall thickness, structure and precision requirements of different parts, adjustments need to be made during processing. The following is an analysis of some casting techniques and key processing points:
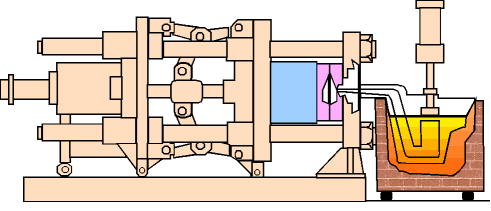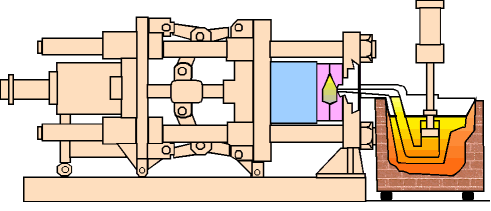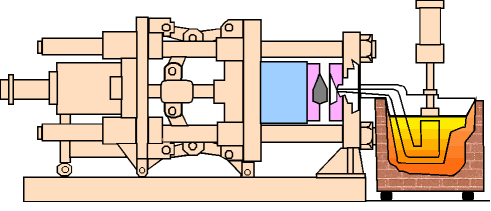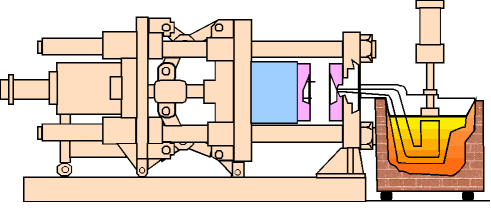
(1) The first is the mold preheating stage
The size of the gearbox housing is large, and the mold needs to be preheated evenly. Too low mold temperature is prone to defects such as cold shut, flow marks and shrinkage, while too high mold temperature will cause sticking and reduced mold life.
Generally, the mold temperature is controlled between 180℃ and 250℃. In addition, the temperature difference should be monitored in areas with more ribs to avoid local solidification too fast.
(2) The second is the smelting and insulation of aluminum alloy.
When die casting gearbox housings, die-cast aluminum alloys such as ADC12 or AlSi9Cu3 are often used. These alloys require the melting temperature to be controlled between 640℃ and 700℃.
Too high a temperature will increase the risk of gas entrainment and form pores; too low a temperature will affect fluidity and lead to incomplete filling. In order to meet the filling requirements of complex structures, appropriate degassing treatment should be carried out to ensure the purity of the alloy.
(3) The third is injection process control, which is the core link of the success of die casting.
Gearbox housings usually have different wall thicknesses and many ribs, which require good filling capabilities. The injection process is divided into two stages: low-speed filling and high-speed filling.
The initial low-speed injection helps the molten metal enter the mold cavity stably to prevent air entrainment; the high-speed stage quickly fills the complex area. The speed is usually controlled at 1-3 m/s and the injection force is controlled at 60-100 MPa.
In order to compensate for the volume shrinkage of the metal during cooling, it is also necessary to apply a holding pressure after the injection and maintain the holding pressure for 2 to 5 seconds. This time can be flexibly adjusted according to the shell wall thickness and structural differences.
(4) Then comes the cooling and solidification stage
The shell structure is variable and the wall thickness is unevenly distributed. If the cooling system is not designed properly, internal stress, shrinkage or thermal cracks are likely to occur.
At this time, a certain cooling method is needed to accelerate the cooling speed of the thick-walled parts and control the solidification sequence so that the metal solidifies sequentially from the far end to the gate to reduce defects.
(5) Finally, demolding and post-processing are carried out.
Because there are a large number of internal and external ribs and mounting holes on the surface of the gearbox shell, demolding requires controlling the mold opening and closing speed and using appropriate demolding agents to avoid sticking or pulling.
After demolding, post-processing steps such as flash removal, X-ray inspection, and dimensional inspection are required to ensure the quality of the shell.
In general, this paragraph is about setting the process parameters in the die casting process according to the structural characteristics of the gearbox housing, what difficult problems need to be considered before processing, and taking appropriate measures to avoid defects during processing to ensure the sealing of the housing.
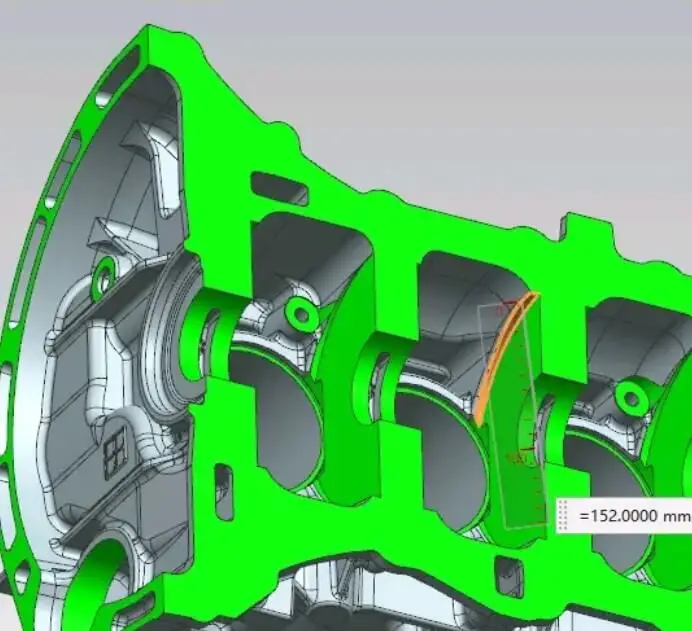
As an experienced metal casting company, we LVXUN have accumulated a lot of practical experience in die casting gearbox housings. Whether it is a complex reinforcing rib structure, a special-shaped cavity, or a part with strict requirements on dimensional accuracy and airtightness, we can optimize and adjust it with mature processes and precise control parameters. We are well aware that quality is the basis of customer trust, and we always adhere to manufacturing parts with technology as the core and quality as the guarantee.
5.What post-processing processes are required for parts after casting? (CNC machining and surface treatment)
After casting, the gearbox housing usually needs to take some machining methods to ensure the dimensional accuracy, form and position tolerances and functional requirements of key parts.
CNC machining not only improves the reliability of the overall assembly, but also lays the foundation for subsequent surface treatment.
First of all, from the perspective of process type, the CNC machining processes commonly used for gearbox housings mainly include the following:
Turning, used to process circular openings and flange end faces on housings;
Milling, widely used to process planes, bosses, ribs and mounting surfaces;
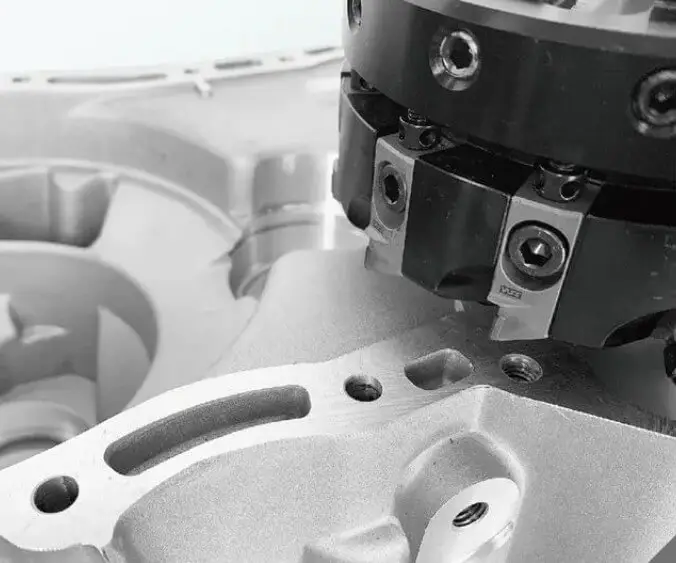

Drilling and tapping, used to process bolt holes, through holes and locating holes;
Boring, used to ensure high-precision coaxiality and dimensional consistency of bearing holes or locating holes in housings;
Five-axis linkage machining, in areas with complex geometric structures, such as internal flow channels, inclined holes or inclined surfaces, helps to achieve multi-faceted machining under one clamping, improving accuracy and efficiency.
After completing the machining, appropriate surface treatment is required according to the use environment and performance requirements to improve its corrosion resistance, thermal stability and appearance quality. Common surface treatment processes include:
Shot blasting or sand blasting, which is used to remove processing residues and improve surface cleanliness, while forming uniform roughness on the surface to enhance the adhesion of subsequent coatings;
Anodizing (especially suitable for aluminum alloy housings), which can form a dense oxide film on the surface to improve corrosion resistance and insulation;
Spraying or powder coating, suitable for housings that require high appearance quality or are exposed to harsh environments for a long time, can provide a variety of colors and protective layer thicknesses;
Impregnation treatment, suitable for castings with micropores, improves the air tightness and liquid tightness of the housing by filling sealing materials to prevent oil leakage;
After reading this, I believe you have already understood the complete process of manufacturing gearbox housings. Here, I need to emphasize that we at LVXUN not only focus on high-quality die casting services, but also provide customers with complete one-stop manufacturing solutions.
That is, whether it is a die casting part with complex structure or a key part with extremely high precision requirements, we can provide you with full process support from prototype to finished product through supporting CNC machining processes and a variety of surface treatment technologies. We have advanced CNC machining equipment and an experienced technical team.
Choosing us means that you only need one supplier to complete the entire process from raw materials to delivery, which greatly saves coordination time, reduces communication costs, and effectively controls the overall manufacturing budget. We are always committed to providing customers with efficient, reliable and worry-free manufacturing services, and are your trusted long-term partner.
6.Summary
Through the combing of the entire process of die-cast aluminum gearbox housing manufacturing, we can see that: whether in material selection, process control or post-processing, every step is crucial to the quality and performance of the final product. Choosing a manufacturer with integrated service capabilities can not only significantly improve efficiency, but also greatly reduce costs and quality risks. If you are looking for a one-stop aluminum die casting parts solution, please feel free to contact us, we will serve you with professionalism and efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Compared with traditional cast iron housing or forged housing, what are the advantages of aluminum die casting?
Compared with cast iron housing, aluminum die casting has obvious lightweight advantages, and its thermal conductivity is better than cast iron, which can better help the internal heat dissipation. Of course, cast iron housing also has its specific application places.
In addition, in terms of process, die casting can achieve one-piece molding of complex shapes and reduce the number of welded or screwed parts. Compared with forgings, die castings have lower costs and higher forming complexity, making them suitable for mass production.
Are gearboxes with bell-shaped housing structures widely used? What is the role of bell-shaped housings?
Gearboxes with bell-shaped housing structures are widely used in traditional automobiles, new energy electric drive systems, and light engineering machinery. The bell-shaped housing is usually located at the front end of the gearbox and is shaped like a bell-shaped housing, hence the name.
In modern manufacturing, bell-shaped housings are increasingly being die-cast as one piece with the main housing, which not only simplifies the assembly process, but also improves overall strength and reliability.