A Guide to Efficient Zinc Die Casting
The zinc die casting process not only meets the demands of manufacturing complex geometries and thin-walled parts, but also offers enhanced aesthetics and durability through a variety of surface treatments. This article systematically introduces the advantages, process steps, and application areas of zinc die casting, providing a reference for design and production.
Table of Contents
1.What is zinc die casting?
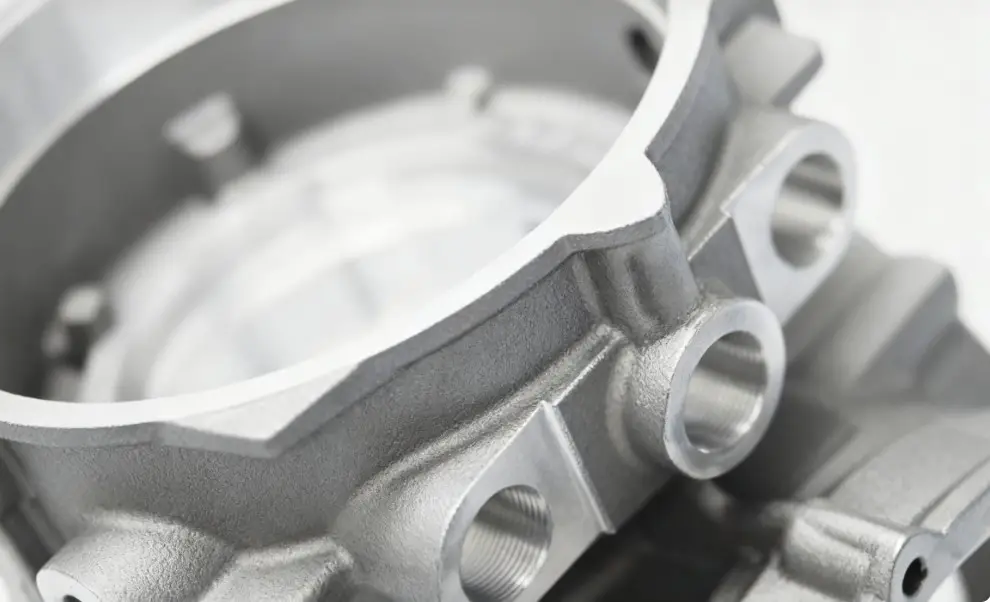
Zinc die casting is a metal forming process in which molten zinc alloy is injected under high pressure into a pre-fabricated precision mold, where it is rapidly cooled to form the desired part.
Due to zinc alloy’s excellent fluidity, ductility, impact resistance, and low melting point, this process is typically performed using hot chamber die casting. Compared to other metals, zinc can be formed at lower temperatures, effectively extending mold life, shortening production cycles, and reducing manufacturing costs.
Due to its high precision, smooth surface finish, and suitability for complex structural parts, zinc die casting is widely used in automotive parts, electronic components, hardware accessories, and other fields.

2.Why choose zinc?
- Low melting point, low energy consumption, high production efficiency
- Economical and efficient, can replace more complex and expensive manufacturing processes
- High strength, good hardness, stable structure
- Excellent electrical and thermal conductivity
- Good corrosion resistance
- High dimensional accuracy and stability
- Excellent thin-wall forming ability
- Possesses cold forming and easy connection characteristics
- Excellent surface finishing performance, suitable for electroplating and decoration
- The material is fully recyclable and environmentally sustainable
3.Zinc alloy for die casting
Common zinc alloys for die casting mainly include Zamak series, ZA series and some special performance alloys such as ACuZinc5 and EZAC. The composition and performance differences of different alloys make them suitable for different application scenarios.
(1) Zamak series (Zamak 2, 3, 5, 7)
The Zamak series is the most commonly used die casting zinc alloy, which is mainly composed of zinc with a small amount of aluminum, copper and magnesium.
- Zamak 2: The highest strength and hardness, suitable for parts with high structural strength requirements, such as automotive and mechanical parts.
- Zamak 3: The most widely used general-purpose alloy, with excellent dimensional stability, fluidity and balanced mechanical properties, easy to electroplate and surface treat.
- Zamak 5: Based on Zamak 3, the copper content is increased, the strength and hardness are higher, and the wear resistance is good. It is currently the most commonly used die-cast zinc alloy in Europe.
- Zamak 7: An improved version of Zamak 3, with a lower magnesium content and better ductility. It is suitable for manufacturing parts with high requirements for formability and surface finish.
(2) ZA series (ZA-8, ZA-12, ZA-27)
The ZA series is a zinc-aluminum alloy with a higher aluminum content than the Zamak series, so it has higher strength and wear resistance.
- ACuZinc5: An alloy developed by General Motors, containing a high copper content, with excellent hardness, creep resistance and dimensional stability, suitable for use in high temperature and high load environments.
- EZAC: A new high-performance zinc alloy with extremely high yield strength and creep resistance, suitable for use in precision mechanical parts with higher requirements.
(3) Special alloys
- ACuZinc5: An alloy developed by General Motors, containing a high copper content, with excellent hardness, creep resistance and dimensional stability, suitable for use in high temperature and high load environments.
- EZAC: A new high-performance zinc alloy with extremely high yield strength and creep resistance, suitable for use in precision mechanical parts with higher requirements.
Summary:
The choice of zinc alloy depends mainly on the application requirements of the product. If precision molding and dimensional stability are emphasized, Zamak 3 or 7 are recommended; if strength and wear resistance are emphasized, Zamak 5 or ZA series can be selected; for high temperature and high load applications, ACuZinc5 or EZAC can be considered.
LVXUN has a wide variety of zinc alloys for casting and a deep understanding of their applications. Therefore, we can provide the appropriate material recommendations for your project.
4.Zinc Die Casting Design Considerations
Uniform Wall Thickness
Maintaining consistent wall thickness reduces porosity, warpage, and stress concentrations. While zinc allows for very thin wall thicknesses, excessive thinness can compromise part strength and durability.
Draft Angle
Designing an appropriate draft angle helps ensure smooth part release from the mold, avoiding damage or surface defects.
Corner Rounding
Avoiding sharp corners and adopting rounded edges or gradual transitions can reduce stress concentrations while improving molten metal flow and filling.
Ribs and Gussets
Adding ribs or gussets can increase part strength and rigidity without significantly increasing weight, making them an effective means of maintaining lightweight and structural reliability.

Machining Allowances and Post-Processing Considerations
Machining allowances should be included in the design to ensure that subsequent processes such as drilling, tapping, and milling can be performed smoothly, ensuring the dimensional accuracy and functionality of the final part.
Optimizing Thin Walls and Complex Structures
Taking advantage of the high fluidity of zinc alloys, thin walls and complex geometries can be achieved, but formability and part strength must be balanced.
5.Zinc Die Casting Steps
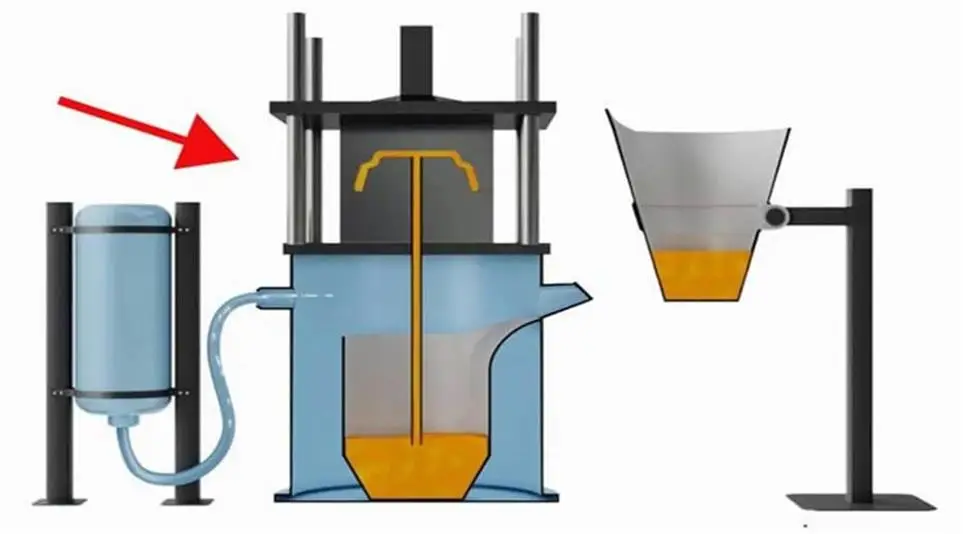
Zinc die casting typically utilizes the hot chamber die casting process, which is renowned for its high efficiency, high dimensional accuracy, and excellent surface quality. While specific operations vary depending on the part structure and equipment type, the overall process remains largely the same, encompassing the following four steps:
Step 1: Mold Preparation
Before die casting begins, the mold must be thoroughly cleaned to remove impurities and residue. Lubricant is then sprayed onto the mold surface to prevent metal sticking. After these preparations are complete, the mold is clamped tightly with high pressure using a hydraulic system to ensure a tight seal during the injection process, preventing metal leakage.
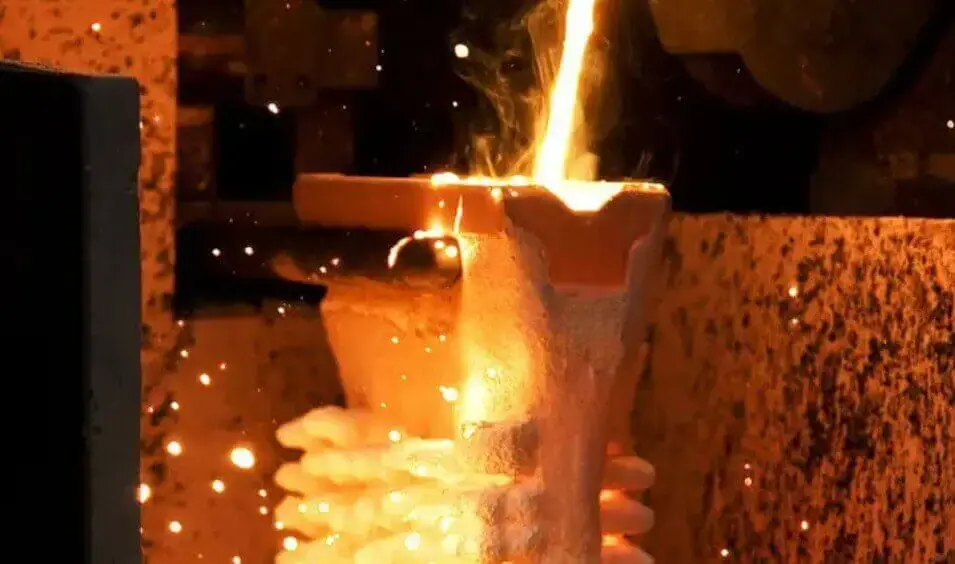
Step 2: Melting and Injection
The zinc alloy is heated to approximately 419°C, melted, and then introduced into the hot chamber injection system. The injection system of a hot chamber die casting machine is located within the molten metal pool, and liquid zinc is pushed into the mold cavity via a feed tube. High-pressure injection (typically in the range of 35–70 MPa) ensures that the molten metal quickly and evenly fills every corner of the mold, resulting in highly precise part shapes.
Step 3: Cooling and Ejection
Once the metal is injected into the mold, it immediately begins to cool and solidify. Cooling time is typically only a few seconds, depending on the wall thickness of the casting and the mold temperature. When the zinc alloy is fully solidified, the mold opens and the casting is ejected by an ejector system. To prevent deformation, the casting must be fully cooled before ejection.
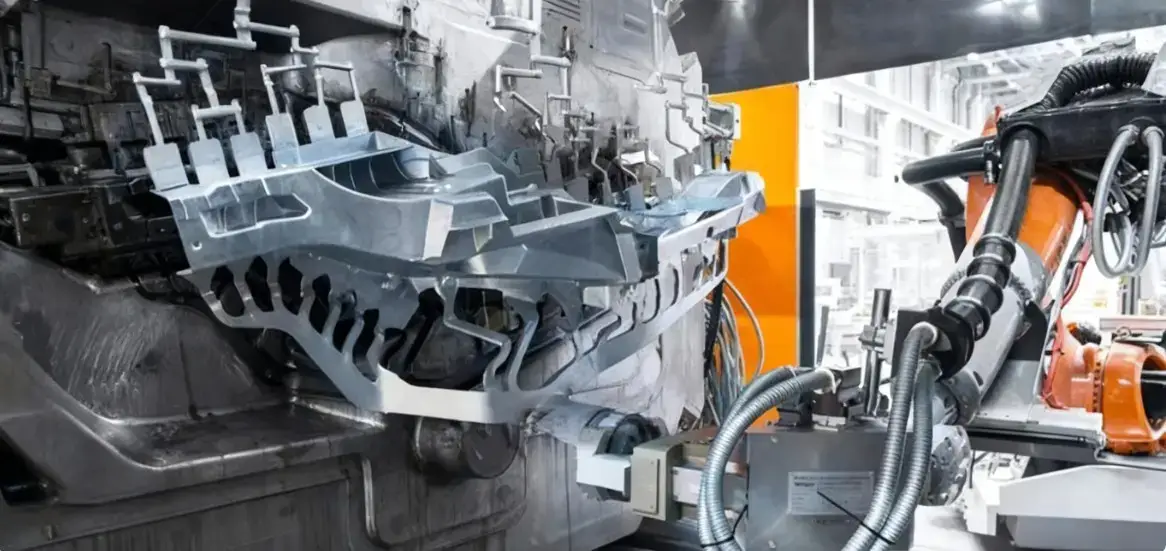
Step 4: Trimming and Recycling
Castings removed from the mold often contain excess sprue, flash, or runner metal. These are removed using mechanical cutting or vibratory deburring equipment. Trimmed zinc alloy scrap can be remelted and recycled, saving both costs and the environment.
6.Surface Treatment Options for Zinc Die Castings
Surface treatment of zinc die castings is primarily used to enhance corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and aesthetics. Different processes are used depending on the intended application. Common surface treatment options include:
- Chromate conversion coating: Forms a protective layer on the zinc surface to prevent corrosion and provides an excellent adhesion base for painting or electroplating.
- Electroplating: Available in nickel, chromium, or copper, it not only improves appearance but also enhances corrosion and wear resistance, making it suitable for both decorative and functional parts.
- Powder coating: Provides a durable, uniform surface with rich colors and resistance to wear and chemicals, making it suitable for parts requiring both aesthetics and durability.
- Paint coating: Provides improved appearance and additional corrosion resistance, with fast production cycles, low costs, and customizable colors.

By selecting the appropriate surface treatment, zinc die casting parts can not only extend their service life but also meet aesthetic, functional, and industry standards.
7.Advantages of Zinc Die Casting
High Strength and Toughness
Zinc alloys offer excellent tensile strength, impact resistance, and toughness, maintaining structural integrity even with thin-walled designs, making them suitable for parts subject to mechanical stress.
Thin Walls, High Precision
High strength allows zinc die casting parts to be designed with thinner walls while maintaining dimensional accuracy and stability. This not only saves material but also reduces die casting costs.
Complex Geometry Casting Capability
Zinc’s high fluidity and wear resistance enable the production of parts with complex shapes and precise structures, eliminating the need for additional components such as bushings or inserts.
Economical and Efficient
Zinc’s low melting point enables the use of hot-chamber, high-pressure injection die casting processes, increasing production speeds. Compared to aluminum or magnesium, zinc die casting offers higher cycle rates and lower energy consumption, reducing both production and post-processing costs.
Extended Mold Life
Zinc alloy’s low melting point and wear resistance extend mold life approximately ten times longer than aluminum molds, reducing mold change frequency and maintenance costs.
Reduced Assembly and Machining
The entire component can be formed in a single step, reducing manual assembly operations. Net-shape casting is also possible, minimizing the need for machining.
Corrosion Resistance and Surface Treatment Versatility
Zinc forms a protective passive layer in atmospheric environments, providing corrosion resistance. Through treatments such as electroplating, spraying, and powder coating, a surface with both decorative and functional properties can be achieved.
Flexible Production Options
Different casting processes can be used to economically produce low, medium, and high-volume parts, depending on the needs.
8.Applications of Zinc Die Castings
Zinc die castings are widely used in various industries due to their high strength, dimensional stability, corrosion resistance, and ability to form complex shapes. Key applications include:
Automotive Industry
Zinc die castings are widely used in the manufacture of automotive interiors and functional components such as bearings, steering systems, brake components, and engine parts. Due to their high strength and excellent wear resistance, zinc alloys (particularly Zamak 2) are often used in areas subject to mechanical stress.

Electronic and Electrical Products
Zinc die castings are suitable for the manufacture of precision electronic components such as switches, regulators, electronic packaging, and connectors. Their excellent dimensional stability and corrosion resistance protect electronic systems from environmental influences. Zamak 3 alloy is widely used due to its balanced properties.
Home Appliances
Zinc die casting is used in home appliance components such as furniture inserts, keychains, shoe buckles, door locks, handles, and belt parts. Its strength and stability ensure product durability and precision.
Mechanical and Industrial
In machinery and engineering equipment, zinc die casting is used for engine parts, gears, and other load-bearing components, leveraging its high hardness and creep resistance to meet structural requirements.
Construction and Hardware
Zinc die casting is used in building hardware for locks, hinges, door handles, and other components, enhancing safety and service life due to its corrosion resistance and high strength.
Consumer Goods and Toys
Zinc die casting can produce toys, hardware, and other consumer electronics components with complex shapes and exquisite appearance, enhancing product appeal and functionality.
9.Conclusion:
Overall, zinc die casting’s combination of high strength, precision forming, rapid production, and low cost makes it a valuable option for modern industrial manufacturing. Whether in the automotive, electronics, or home appliance industries, proper material selection and process design can maximize the performance value of zinc die casting.
FAQs:
How does the strength of zinc die castings compare to aluminum alloys?
Zinc alloy die castings generally have higher strength and toughness and are suitable for applications requiring high strength.
Can zinc die castings be welded or repaired?
Zinc die castings are not easily welded, but they can be repaired through machining.
What is the production cycle and cost of zinc die castings?
Zinc die castings have a short production cycle and relatively low cost, making them suitable for high-volume production.
What industries are zinc die castings suitable for?
Zinc die castings are widely used in industries such as automotive, electrical, home appliance, construction, medical, and consumer goods.
What is the corrosion resistance of zinc die castings?
Zinc alloys have good corrosion resistance, making them particularly suitable for outdoor and humid environments.