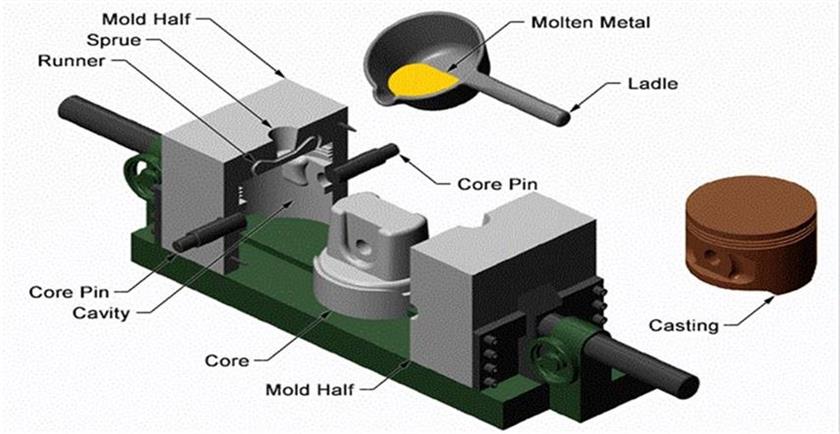
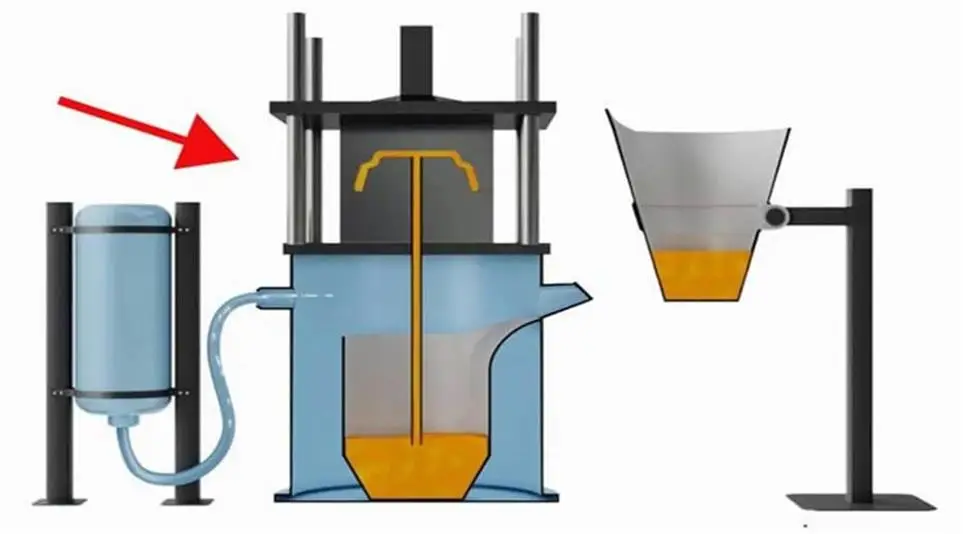
Gravity Casting: Choose the Right Process for Your Parts
When faced with the choice of structural casting solutions, many people often struggle with “die casting or gravity casting”? “Is sand casting cheaper”? “Which parts are suitable for gravity casting”?
Fortunately, LVXUN has rich manufacturing experience in these three casting processes. We have been committed to providing our customers with high-quality castings for many years. If you want more professional advice, you can contact us at any time.
Of course, this article mainly introduces gravity casting, but after reading it, you will also have some understanding of sand casting and die casting, and through comparative analysis of the processes, it will help you to choose the right process. The following will be formally read:
1.What is gravity casting?
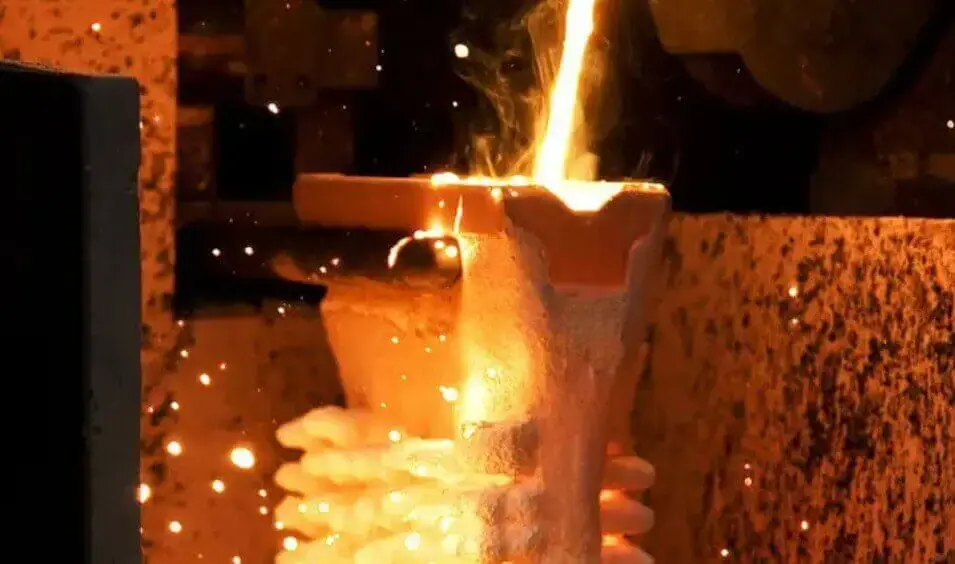
Gravity casting is a metal forming process that uses the gravity of molten metal to fill the mold. It is one of the traditional casting methods. Its core feature is that it does not require external pressure, and only relies on the gravity of the molten metal to complete the filling, solidification and forming.
Unlike casting methods that rely on external forces (such as die casting that relies on pressure and centrifugal casting that relies on centrifugal force), gravity casting relies on natural drop to complete metal filling, and no additional pressure is involved in the forming process.
Types of gravity casting
The following will be divided into two types: conventional metal mold gravity casting (also known as permanent mold casting) and innovative tilted pouring gravity casting (also known as tilted casting).
(1) Metal mold gravity casting:
The use of reusable metal molds can provide higher dimensional accuracy and better surface quality, suitable for medium-volume production.
(2) Tilt pouring gravity casting:
The tilted casting mold pours the molten metal in a tilted state, which helps to reduce turbulence and oxidation and improve the quality of the casting. It is often used in the production of thin-walled parts or high-precision parts.
2.Gravity casting operation process
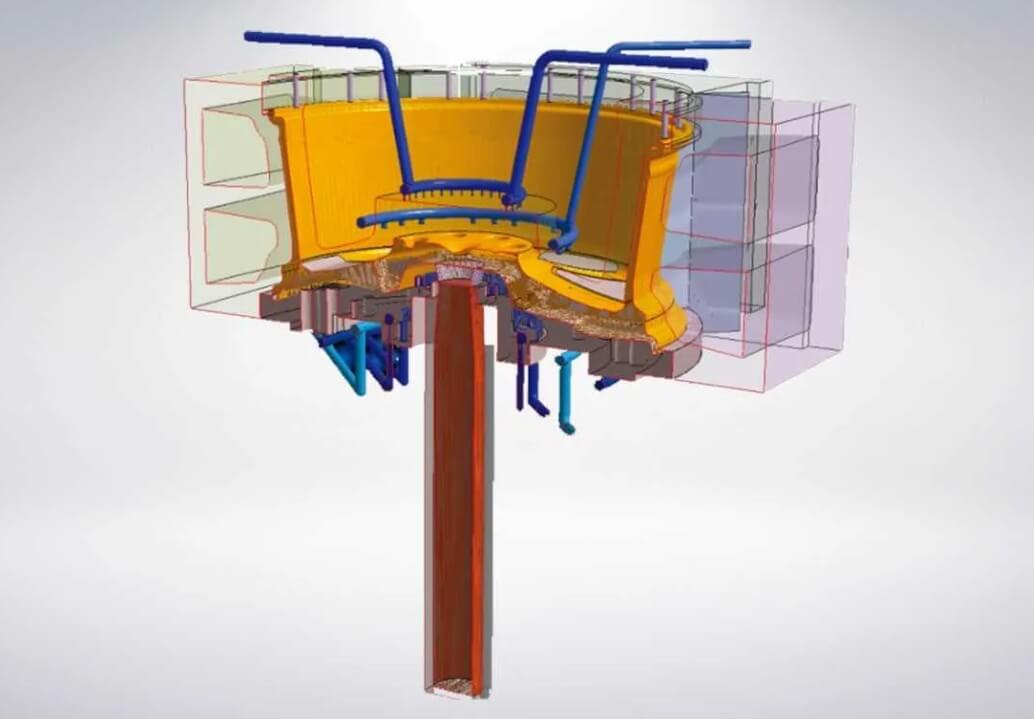
Simulation of internal structure of gravity casting
[ Mold preparation ]
↓
Use a metal mold, preheat it to the appropriate temperature and apply a release agent to improve the casting quality and demolding efficiency.
[ Alloy Melting ]
↓
Melt the metal raw materials (such as aluminum alloy, copper alloy, etc.) in a melting furnace and remove the slag and gas.
[ Pouring Metal ]
↓
Use gravity to pour the molten metal directly from the ladle into the metal mold without pressurization, and control the pouring speed to prevent air entrapment.
[ Cooling and Solidification ]
↓
The metal cools naturally in the mold to form the required casting shape. Controlling the cooling rate can optimize the structure and performance.
[ Opening the Mold and Taking Out the Casting ]
↓
After the casting cools to a certain temperature, open the mold and take out the casting to check whether it is complete and whether it is sticky.
[ Cleaning and Cutting ]
↓
Remove the gate, riser, flash and other attached parts, and clean the surface oxides or residues.
[ Heat Treatment (if necessary) ]
↓
According to the material and use requirements, perform aging treatment, solution treatment, etc. to improve the mechanical properties.
[Subsequent processing and inspection]
↓
If necessary, perform machining, such as milling, drilling, etc., and perform quality inspections such as dimensional inspection and flaw detection.
[Finished product storage]
↓
Qualified gravity castings are classified and packaged, ready for storage or delivery to customers.
3.Gravity casting, die casting, sand casting, how should these three processes be selected?
Comparative analysis of gravity casting, die casting and sand casting:
(1) Compared with die casting:
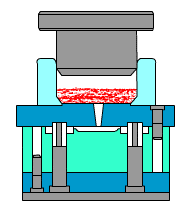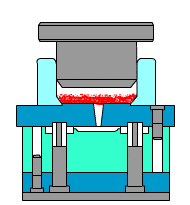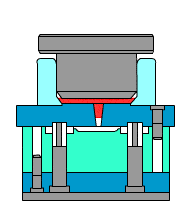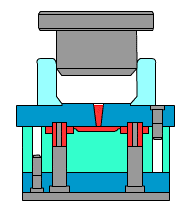
Die casting:
relying on pressure,
filling quickly
Die casting requires special high-pressure equipment and precision molds. The metal liquid quickly fills the cavity with high speed and high pressure. This process is suitable for structural parts with batch production and complex thin-walled requirements. For example, thin-walled parts such as mobile phone cases and motor housings are very suitable for die casting.Gravity casting is a slow process that completely relies on natural gravity to form.
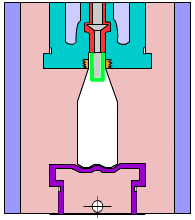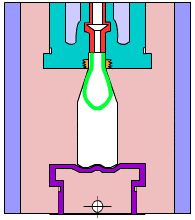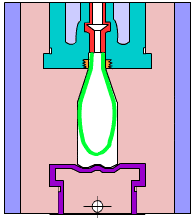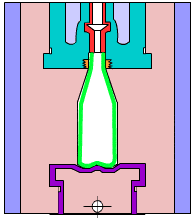
Gravity casting:
relying on gravity,
slow molding
But one thing needs to be noted. Die casting generally uses specific aluminum alloys (such as ADC12), which are not suitable for heat treatment, and the finished product has the risk of pores. Gravity castings can be heat treated. For example, A356 alloy can obtain better strength after heat treatment, which is suitable for load-bearing structural parts.
(2) Compared with sand casting:
Sand casting molds are disposable sand molds, which are suitable for trial production and low-volume production of large or complex parts, but their dimensional accuracy and surface quality are poor, and the consistency of castings is also low. Gravity casting uses metal molds, which have high repeatability and better surface quality. It is suitable for medium batches and application scenarios that require dimensional accuracy.
Summary:
In summary, gravity casting is a process between low-cost sand molds and high-efficiency die casting. It has high cost performance and good process stability. If you pursue medium output, medium cost and high surface quality, then gravity casting is very suitable for producing your parts.
If you are still a little entangled, you can also compare the content to be introduced below to see if there is your part. If so, there is no need to entangle it. Choosing gravity casting is the right solution. If your part is not available, you can consult LVXUN’s professional engineers. We will give you professional answers and provide high-quality one-stop services.
4.What types of parts are gravity castings suitable for?
Gravity casting is widely used in parts with medium complexity, moderate strength requirements and high dimensional accuracy, especially in the following categories:
(1) Automotive parts:
Cylinder heads, suspension brackets, steering knuckles, wheel hubs, etc. These parts require a certain degree of density and strength, and their shapes are not too complicated.
In addition, as we mentioned above, gravity castings can be heat treated compared to die castings, which is suitable for use in the automotive field, which is a structural part that needs to bear a certain load.
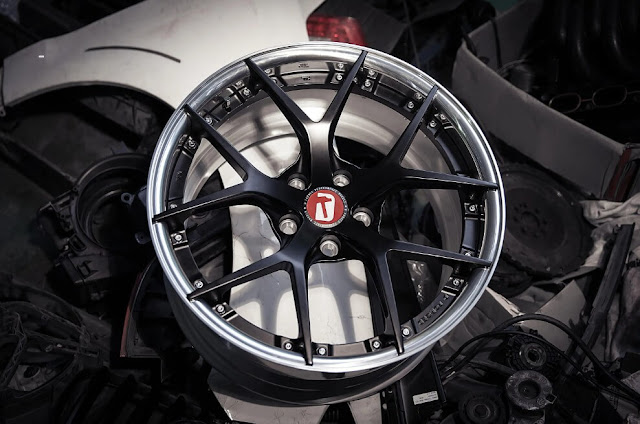

Car wheels
(2) Aviation and aerospace structural parts:
A356-T6 gravity castings are often used in small aircraft brackets, shells, seat rings and other parts. They have a light structure and moderate cost. By controlling the porosity and coordinating the heat treatment process, they can fully meet the quality and safety requirements of the aerospace industry.
(3) Engineering machinery and hydraulic parts:
Pump housings, valve bodies, hydraulic joints, the most important point of these parts is that the parts need to be strong, can be used in high-pressure liquid environments and will not have problems for several years.
(4) Consumer durable equipment:
Motorcycle parts, bicycle aluminum alloy frames, small engine parts, etc. These parts need to have good mechanical properties.
Summary:
In general, gravity casting is an ideal manufacturing method for parts that require medium batches, high consistency, good mechanical properties and post-processing performance.
5.Advantages of gravity casting in forming thick-walled and special-shaped structural parts
We all know that die casting is good at making thin-walled parts, so what casting process is suitable for thick-walled parts?
Gravity casting uses the molten metal to flow naturally into the mold cavity under the action of gravity, and then cool and solidify to form. This seemingly “primitive” method shows natural adaptability when dealing with complex thick-walled structures.
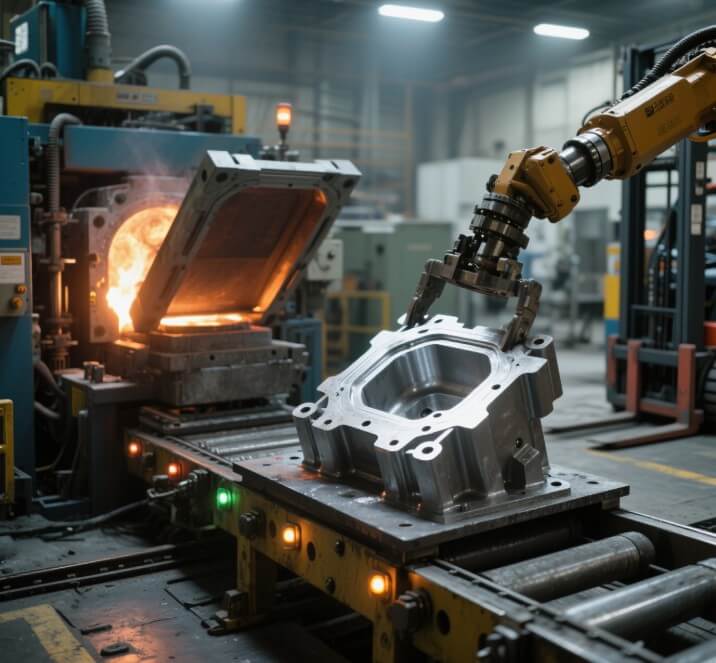

A group of thick-walled parts are being produced on a gravity die casting machine
(1) The natural filling process is more suitable for thick-walled and special-shaped parts
Due to the low flow rate of the molten metal and the long free filling time, gravity casting can better adapt to structural parts with large wall thickness differences and complex internal cavities, reducing defects such as turbulence and gas entrapment.
Compared with the risk of metal splashing and pores caused by high-speed jet filling during die casting, the gravity casting process is more gentle and stable.
(2) Low mold stress is conducive to dimensional stability
In large-scale casting, mold thermal expansion and cooling deformation are common problems. Gravity casting does not rely on high-pressure drive, the mold bearing stress is lower, and the temperature rise is slow, which helps to improve dimensional accuracy and repeatability.
(3) Gravity castings are often evenly stressed and have good shrinkage control
Complex structural parts often have thick supporting parts, thin-walled transition areas, and large-area connection structures. If the cooling rate is inconsistent, cracks, deformation, or shrinkage defects are likely to occur.
When performing metal gravity casting, the riser and chill can be reasonably designed in the thick-walled area to reduce the risk of metal casting shrinkage.
In addition, long solidification time helps to uniformly cool, reduce thermal stress concentration, and reduce the probability of casting deformation.
6.What metal materials can be used for gravity casting? Which aluminum alloy is the most common?
Gravity casting is suitable for a variety of non-ferrous metal alloys, including aluminum alloys, copper alloys and other metals.
Compared with die casting, gravity casting has a wider adaptability to aluminum alloy materials and can use some aluminum alloys that cannot be die cast.
Main materials that can be used for gravity casting include:
(1) Aluminum alloy (most commonly used)
A356 (AlSi7Mg): the most common aviation-grade aluminum alloy, with good casting fluidity and high strength after heat treatment.
A319 (AlSi5Cu3): has good thermal crack resistance and dimensional stability, suitable for high-temperature parts.
A413 (AlSi12): has excellent fluidity and is suitable for thin-walled structures, but its strength is slightly lower than that of A356.
ZL101, ZL102 (Chinese standard): widely used in automobiles, motorcycles, and mechanical structural parts.
535 (AlMg5Si): has excellent corrosion resistance and is suitable for marine and transportation parts.
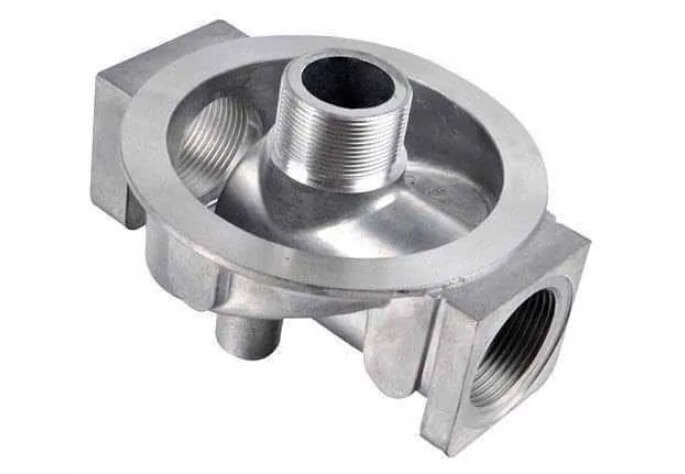

Aluminum alloy gravity castings
(2) Copper alloy:
Common ones include tin bronze and aluminum bronze, suitable for occasions with high requirements for wear resistance and conductivity, such as pump bodies, valves, electrode seats, etc.
(3) Magnesium alloy:
Although magnesium alloy has a low melting point and is highly reactive, its lightweight properties also allow it to be used on a small scale in some lightweight applications.
Summary:
Among aluminum alloys, A356 is currently one of the most commonly used gravity casting aluminum alloys. It is widely used in aviation, automobiles, and industrial structural parts because of its good fluidity, heat treatment performance, and comprehensive mechanical properties.
7.Why is gravity casting sometimes chosen over die casting?
Although die casting is efficient and suitable for mass production, it is not suitable for all applications. The following are typical reasons for choosing gravity casting:
(1) Alloy selection is more flexible:
Die casting has great restrictions on alloys. Some high-performance aluminum alloys cannot be die cast, while gravity casting can use almost all mainstream aluminum alloys and supports heat treatment. If you want to know which alloys are suitable for die casting, you can refer to the content of this article, which I believe will be helpful to you.
Among them, the biggest advantage of gravity casting is that the castings can be heat treated and have excellent mechanical properties:
Die castings are prone to expansion and cracking during heat treatment due to the large number of internal pores; while gravity castings have high density and higher strength after heat treatment, making them more suitable for load-bearing parts.
(2) Relatively low mold cost:
Die casting molds are expensive and require large initial investment, which is suitable for million-level production; while gravity casting molds are moderately priced and suitable for medium-volume manufacturing of thousands to tens of thousands of pieces.
(3) Fewer internal defects:
Gravity castings are easier to obtain low-porosity, high-density structural parts due to their slow pouring speed and reasonable mold ventilation design.
(4) Strong adaptability to size and wall thickness:
Die casting is more suitable for thin-walled parts, while gravity casting is more suitable for medium-thick walls and high structural strength requirements. These two processes each have their own application environment and manufacturing advantages.
8.Summary
No casting process is omnipotent. Whether it is die casting, low-pressure casting, investment casting, or gravity casting, which is the focus of this article, they all have their own advantages and areas of expertise, so it is crucial to choose the right casting process and manufacturer for your parts.
Through the analysis above, we know that gravity castings are suitable for structural parts, aviation aluminum castings, automotive parts and other fields. The cost-effectiveness and performance stability it reflects often exceed expectations.
Truly understanding its characteristics and applicable boundaries will help you make clearer and more secure decisions in product development or technology selection. In addition, we at LVXUN will provide you with one-stop services for die casting, low-pressure casting, investment casting and gravity casting, and create exclusive manufacturing solutions for your parts.