Expendable Mold Casting vs Non expendable Mold Casting: Definition, Types, Pros and Cons, and Applications
When choosing the right way to make your parts, you may hear words like “expendable mold casting”, “non expendable mold casting”, “permanent mold casting”, etc. It sounds like a professional term, and it is, but behind it is actually a very practical casting process.
Expendable mold casting, such as our most common investment casting process; non expendable mold casting, also called permanent mold casting, such as our most common die casting process. So in this article, we will take you to understand the true meaning of these terms, their application value in metal forming, and help you make wise manufacturing decisions.
Table of Contents
1.What is expendable mold casting?
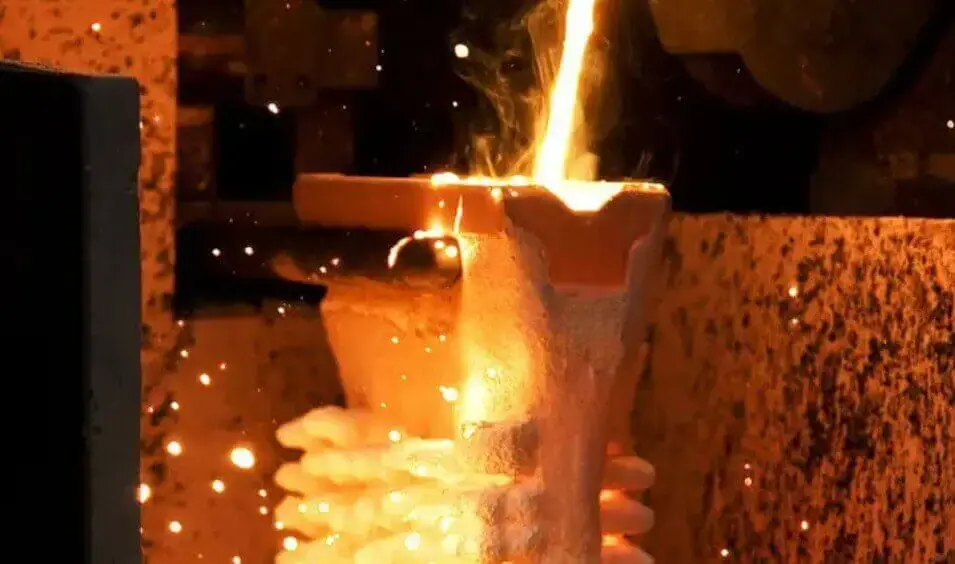
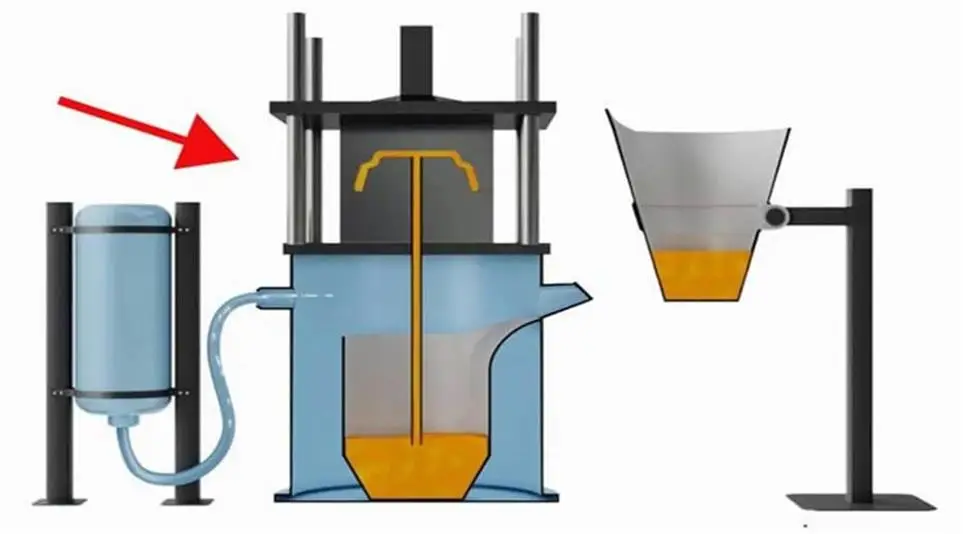
Expendable mold casting is a casting process that uses disposable molds to make metal parts. Unlike reusable metal molds, the molds used in this process will be destroyed after casting and cannot be used again.
The mold is usually made of materials such as sand, plaster, ceramic or wax. These materials have good plasticity and can accurately replicate the complex details of the model, so they are very suitable for manufacturing metal parts with complex geometric structures and delicate surface contours.
2.Basic process of expendable mold casting process
First, a model is made according to the part design. The model material is mostly wax or plastic, which can be easily melted or decomposed in subsequent processing; then the model is used to make the mold, and the model is removed by heating or chemical means to form a cavity; then the molten metal is poured into the mold, and after it cools and solidifies, the mold is broken or removed to remove the casting. The whole process is simple and efficient, and is suitable for the processing of a variety of metal materials such as aluminum alloy, stainless steel, carbon steel, etc.
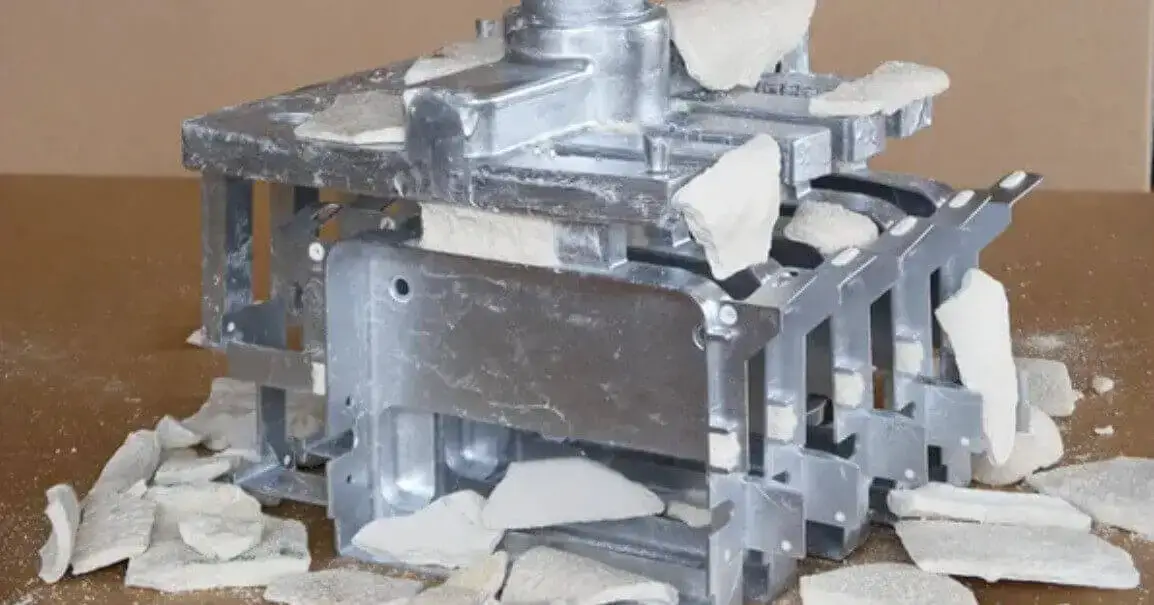

Since each part needs to make a separate mold, this process is not suitable for mass production, but it has obvious advantages in small-batch manufacturing, complex part development or functional prototyping.
3.Advantages and disadvantages of expendable mold casting
Advantages
Flexible process: It can produce parts with complex shapes, multiple internal cavities, and rich structural details.
Low cost: The mold is made of cheap materials such as sand, gypsum, ceramics, wax, etc., and the mold making cost is low.
Excellent surface quality: The use of shell molds or investment molds can obtain a smoother surface, reducing the need for subsequent processing.
Wide range of material applications: Almost all metals (aluminum, copper, iron, magnesium, and even high-temperature alloys) can be cast using this process.
Disadvantages
The mold is not reusable: The mold used for casting needs to be broken or burned after each use and is usually not used a second time.
Some casting processes have limited precision: the surface of sand molds and other molds is rough, and the dimensional accuracy and consistency of castings are lower than metal molds, and post-processing may be required.
Slow production speed: Each piece needs to be made with a new mold, which is not suitable for mass production and has a long cycle.
4.What is non expendable mold casting?
Above we introduced the definition, process flow, advantages and disadvantages of expendable mold casting, so everyone should also want to ask what is non expendable mold casting? What is the difference between it and expendable mold casting?
Similar to expendable casting, non expendable mold casting, also known as permanent mold casting, involves pouring molten metal into a mold of the desired shape and then allowing it to solidify to form a casting.
However, the difference between the two is that the mold in non expendable mold casting is not destroyed after each casting, but can be reused over and over again in multiple production cycles, which is why the process is also called permanent mold casting.
Permanent metal molds are usually made of high-strength, heat-resistant metal materials (such as cast iron, steel or copper alloys) that can withstand repeated pouring of high-temperature molten metal without serious deformation.
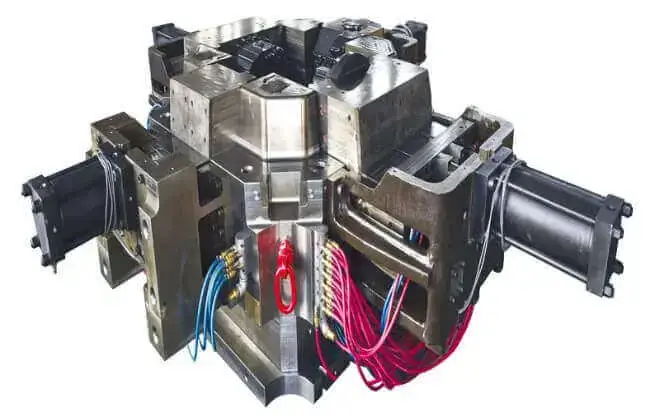

For the complete process flow and more information about non expendable mold casting, that is, permanent mold casting, please refer to this article. Here we briefly explain the advantages and disadvantages of non expendable mold casting:
Advantages include:
High dimensional accuracy
Near net shape can be achieved
Suitable for mass production
Good casting strength
Reusable mold
Less waste
Disadvantages include:
High mold cost
Not suitable for small batch production or not economical when small batch production is used
Limited complex structure design, requiring the use of movable core
More suitable for low melting point metals, high melting point metals have greater wear on the mold
5.Common expendable mold casting examples
There are many types of expendable mold casting technology, each with its own unique characteristics and advantages. Some of the most common types of expendable mold casting include:
Sand casting:
This is the oldest and most widely used casting method. Sand is compacted around the model using a binder (such as clay), and the model is removed to form a cavity, and finally the molten metal is poured. Suitable for large-sized, high-temperature resistant metals, and parts with simple structures or medium precision requirements, with rough surfaces and general tolerances.
Shell casting:
It is an improved sand casting that uses resin-covered sand to form a thin shell on the heated model, usually 5-10 mm thick. Compared with traditional sand molds, it has higher precision and smoother surface, but the mold cost is slightly higher.
Investment casting:
Also known as lost wax casting, it is a precision casting process in which a wax mold is coated with a ceramic shell layer and then the wax mold is removed to obtain a cavity. This process can achieve high precision and high finish, and is suitable for complex structures, thin-walled or high-performance alloy parts.
Plaster casting:
The mold is made of gypsum instead of sand. Gypsum has good fluidity and can replicate fine geometry and textures. The precision and surface quality are better than sand molds, but the mold is fragile and slow, and it is not suitable for high melting point metals.
Lost foam casting:
The model is made of foam plastic (such as polystyrene), and the model does not need to be removed before pouring; the molten metal directly contacts the foam, and the foam evaporates to form a cavity. The process can achieve complex overall shapes without mold extension, and the accuracy and surface quality are between sand molds and investment molds.
Above we have introduced the expendable mold casting example process in detail, so in order to help you further understand and compare, we will also introduce the non expendable mold casting example process below.
6.Common non expendable mold casting examples
Gravity casting
Use gravity to pour molten metal directly into a pre-heated metal mold (usually steel or cast iron). Due to the fast heat conduction of the mold, the casting cools quickly, the grains are fine, the surface is smooth, and the size consistency is good. This method has a simple structure and low cost, and is suitable for medium and large production scenarios.
Die casting
The molten metal is injected into the metal mold by high pressure, the pressure is maintained until the metal solidifies, and then the part is ejected. This technology can produce parts with complex shapes and excellent surface quality. At the same time, its biggest advantage is that the production efficiency is extremely fast, and it is particularly suitable for mass production of aluminum castings and zinc castings.
Low pressure casting
Using low air pressure to push metal into the mold cavity from the bottom, this process can effectively avoid gas inclusions and ensure consistent filling compared to die casting. It is suitable for thin-walled, complex structural parts, with high casting density and better mechanical properties than gravity casting, but the manufacturing cycle is lower than high-pressure casting.
Centrifugal casting
Centrifugal casting is a process in which molten metal is poured into a high-speed rotating cylindrical mold to form a casting with the help of centrifugal force. The molten metal is evenly distributed along the direction of the centrifugal force. This method is suitable for manufacturing pipes or cylindrical parts with good mechanical properties and uniform wall thickness, with high process efficiency and stable part quality.
Continuous casting
A continuous semi-solid billet is formed by continuously pouring molten metal into a water-cooled metal mold, which is then cut into segments or further rolled and stretched into wire, plate, etc. It is suitable for high-volume production, with uniform billet quality and consistent structure, but the equipment is complex and the investment is large.
7.Expendable mold casting vs non expendable mold casting
The following is a summary of the comparison between expendable casting (disposable mold) and non expendable casting (permanent mold) in terms of cost, production efficiency, surface quality and material adaptability:
Cost
The mold making cost of expendable casting is low, usually using cheap materials such as sand, plaster, wax or ceramic, but each piece requires a new mold, resulting in a higher unit cost.
The mold of non expendable casting (permanent mold casting) (such as steel mold or cast iron mold) has a high initial investment, but because it can be reused thousands of times, the unit cost is significantly reduced when the batch is large, and it is more economical.
Production speed and efficiency
Expendable casting takes time to make and destroy the mold, so the total cycle is longer. Non expendable casting has a fast cycle, and a single piece takes only 20 seconds to 5 minutes, and can realize automatic pouring and ejection, which is suitable for medium and large-scale production.
Surface finish and dimensional accuracy
The precision and finish of expendable casting vary greatly: sand casting has the lowest tolerance and precision, investment casting has the highest tolerance and precision, and the surface finish exceeds that of non expendable casting.
Non expendable casting processes generally have high precision and excellent surface finish. The tolerance extreme precision range values are not much different.
Material adaptability
Expendable casting can handle a wide range of metals, including low melting point alloys to high temperature alloys, such as steel, titanium, and nickel-based alloys. Non expendable casting is only suitable for low melting point non-ferrous metals, such as aluminum, magnesium, copper, and zinc alloys, because high temperature will aggravate mold wear and shorten life.
Summary
Expendable casting is suitable for complex structures, low batches, high temperature materials, and cost-flexible manufacturing needs. Non expendable casting is suitable for medium and high batches, high precision and high efficiency. So based on the above introduction, we can conclude that these two casting methods are suitable for different application scenarios. Below we will introduce their application scenarios.
8.Differences in application scenarios between expendable mold casting and non expendable mold casting
Application scenarios of expendable mold casting
Expendable mold casting (disposable mold) is often used to manufacture parts with complex structures, small batches or high requirements for material types:
Automotive industry: expendable molds are suitable for the needs of automotive parts with complex structures and diverse materials, such as cylinder heads, brake drums, intake manifolds and other structural parts.
Aerospace: Production of high-precision, high-temperature alloy parts such as turbine blades, impellers, fuel system components, etc., investment casting is particularly suitable for complex blade shapes.
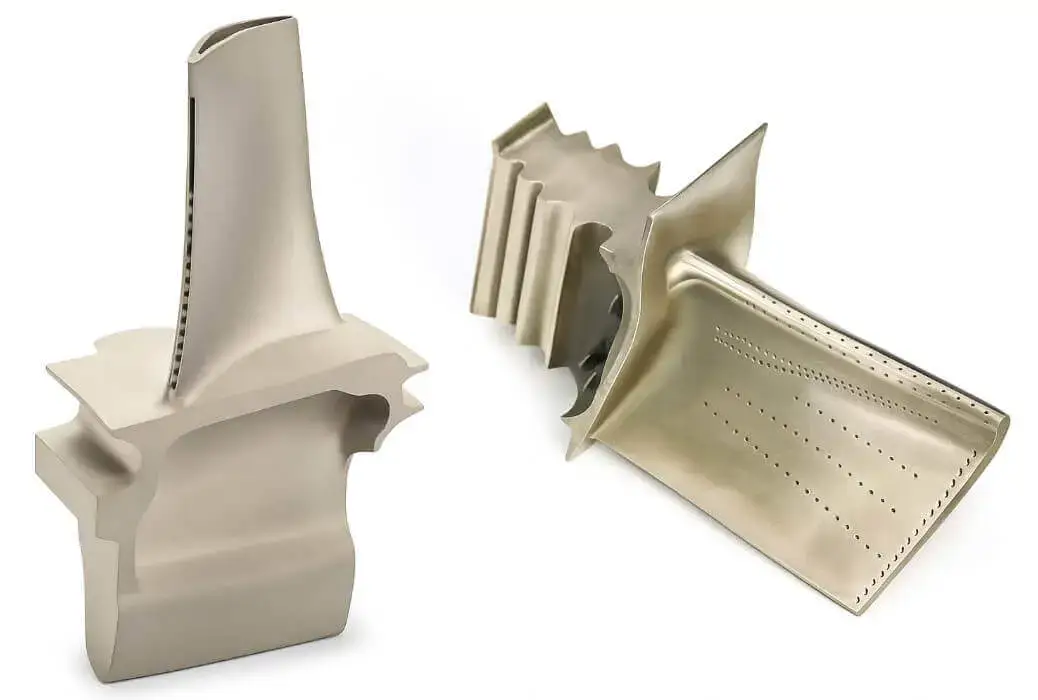
Energy and heavy industry: Such as wind power, oil and gas, pump housings, gearboxes, large housings in heavy machinery, etc., are manufactured by sand mold or investment casting process.
Medical devices and prostheses: used for implants, medical devices with complex internal structures, especially parts with high requirements for material biocompatibility.
Jewelry and art sculptures: Investment casting is often used for bracelets, silver and copper sculptures and other parts with fine textures and decorations.
Application scenarios of non expendable mold casting
Non expendable mold casting (permanent mold casting) is widely used in fields with high requirements for dimensional consistency, surface quality, and cost efficiency:
Automobile manufacturing: production of transmission housings, suspension components, etc., for large-scale, stable quality structural parts.
Aerospace and defense: commonly used to manufacture structural parts, radiators, pump bodies, shipborne equipment, etc., to meet high reliability standards.
Industrial machinery and energy equipment: valves, pump bodies, compressor parts, pump housings, gears, bearing housings, etc. require wear-resistant and high-performance mechanical parts often use this method.
Household and consumer products: including high-quality kitchenware, electrical housings, plumbing accessories, toys and other products, requiring smooth surfaces and consistent appearance.
Electronic and electrical components: manufacturing connectors, radiators, motor housings, plugs and sockets and other parts, requiring high precision and conductive/insulating properties.
Ship and marine hardware: casting pump housings, propeller structural parts, water pipe fittings, etc., often using aluminum and copper alloys to maintain corrosion resistance.
Building, HVAC: manufacturing heat exchanger supports, fan impellers and control valves for industrial and civil building systems.
Having read this far, we hope that you have understood the common processes of expendable mold casting and non expendable mold casting, their advantages and disadvantages, and some of their common application industries and scenarios. If you are looking for a metal processing manufacturer, you can fully trust our capabilities.
We LVXUN can provide one-stop metal parts production services, covering the whole process solution from preliminary casting to finished product processing. Whether it is investment casting, die casting, or other common precision casting processes, we have a mature production system and rich experience.
At the same time, we can also provide subsequent CNC machining, heat treatment and surface treatment services according to customer needs, such as sandblasting, electroplating, oxidation, etc., to ensure that the parts meet the standards in terms of dimensional accuracy, mechanical properties and appearance quality. Whether it is small batch customization or large-scale production, we can meet the diverse needs of various industries for metal parts in a flexible and efficient way.

FAQ:
Why can’t expendable molds be reused?
Expendable molds are not usually reused because they can cause tiny cracks in the mold when the metal is poured in, they break when the metal hardens, and they usually need to be broken to remove the casting. For these three reasons, the molds used for expendable mold casting are disposable.
Which process is more economical?
Expendable mold casting is more cost-effective for small batches; in large batches, non expendable molds have a lower cost per piece because the molds can be reused.
Which method has higher precision?
Investment casting performs better in terms of accuracy and detail replication, but die casting has obvious advantages in terms of dimensional consistency.
What materials can expendable molds be used to produce?
Almost all metals can be used, such as aluminum, copper, steel, titanium, etc., especially for high-temperature alloys that are difficult to die-cast.
What materials are non expendable molds suitable for?
Mostly used for low-melting-point alloys such as aluminum, zinc, and magnesium. High-melting-point metals have a short service life or are not suitable.
Which method is more environmentally friendly?
Non expendable mold processes have less waste because the molds can be reused; while expendable molds need to be re-molded, which may generate more waste.
Is machining required after casting?
In most cases, a small amount of machining is still required, especially in areas with high dimensional tolerances or fit requirements.
How to choose a suitable casting process?
Comprehensive judgment based on the complexity of the part structure, production batch, materials used, dimensional tolerances and budget.